TIME DEPENDENT SCHRODINGER WAVE EQUATION :
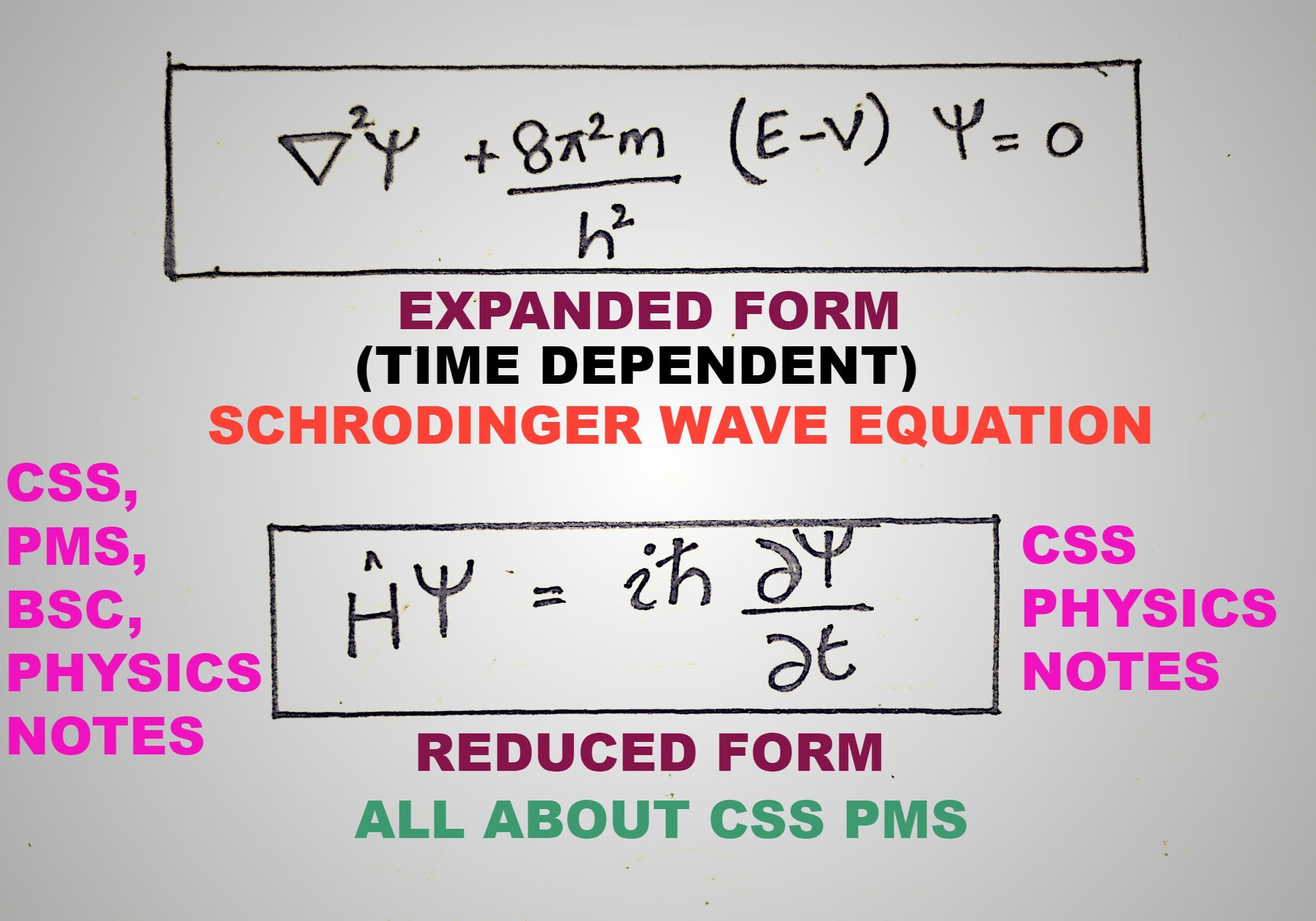
The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation is a fundamental concept in Quantum Mechanics that describes the time-evolution of a quantum system. It is a partial differential equation that relates the wave function of a system to its energy and time.
Mathematical Formulation:
The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation is written as:
iℏ (∂ψ/∂t) = Hψ
where:
ψ (psi) is the wave function of the system, which describes the quantum state of the system- t is time- H is the Hamiltonian operator, which represents the total energy of the system- i is the imaginary unit (i = √(-1))- ℏ is the reduced Planck constant (ℏ = h/2π, where h is the Planck constant)- ∂/∂t is the partial derivative with respect to time
Derivation :
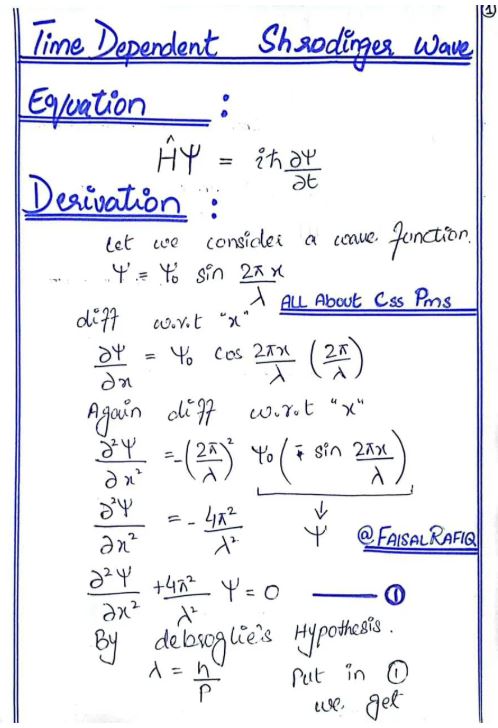


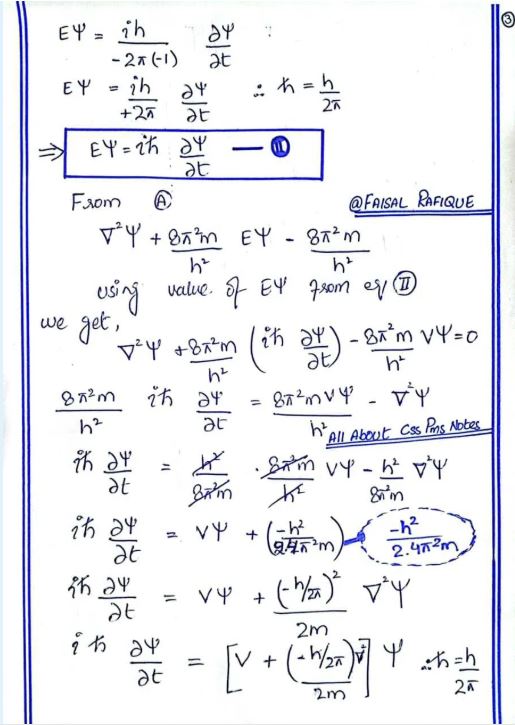
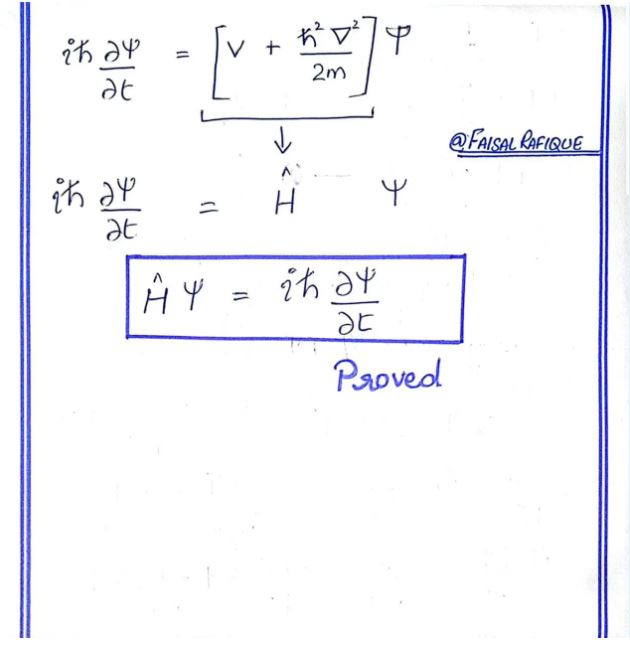
Physical Interpretation :
The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation describes how the wave function of a system changes over time. The equation states that the time-derivative of the wave function is proportional to the energy of the system, as represented by the Hamiltonian operator.
In other words, the equation describes how the quantum state of a system evolves over time, taking into account the interactions between the system and its environment.
Key Features :
1. Linearity: The equation is linear in ψ, meaning that the sum of two solutions is also a solution.
2. Time-reversal symmetry: The equation is symmetric under time reversal, meaning that if ψ(t) is a solution, then ψ(-t) is also a solution.
3. Unitarity: The equation preserves the norm of the wave function, meaning that the probability of finding the system in a particular state is conserved over time.
Solving the Equation:
The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation can be solved using various methods, including:
1. Separation of Variables: This method involves separating the wave function into a product of spatial and temporal components.
2. Fourier Transform: This method involves transforming the wave function into the frequency domain using the Fourier transform.
3. Numerical Methods: This method involves using numerical algorithms to solve the equation, such as the finite difference method or the finite element method.
Applications:
The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation has numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Quantum Mechanics: It is used to study the behavior of quantum systems, such as atoms, molecules, and solids.
2. Chemical Physics: It is used to study chemical reactions and the behavior of molecules in different environments.
3. Optics: It is used to study the behavior of light and its interactions with matter.
4. Condensed Matter Physics: It is used to study the behavior of solids and liquids, including superconductors and super fluids.
Examples :
- Particle in a Box : The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation can be used to study the behavior of a particle in a box, where the particle is confined to a specific region of space.
- Harmonic Oscillator: The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation can be used to study the behavior of a harmonic oscillator, where the particle is subject to a restoring force proportional to its displacement.
- Quantum Tunneling: The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation can be used to study the behavior of quantum tunneling, where a particle can pass through a potential barrier even if it doesn't have enough energy to classically overcome the barrier.
In summary, the Time-Dependent Schrödinger Wave Equation is a fundamental concept in Quantum Mechanics that describes the time-evolution of a quantum system. Its solutions provide valuable insights into the behavior of quantum systems and have numerous applications in various fields of physics and chemistry.