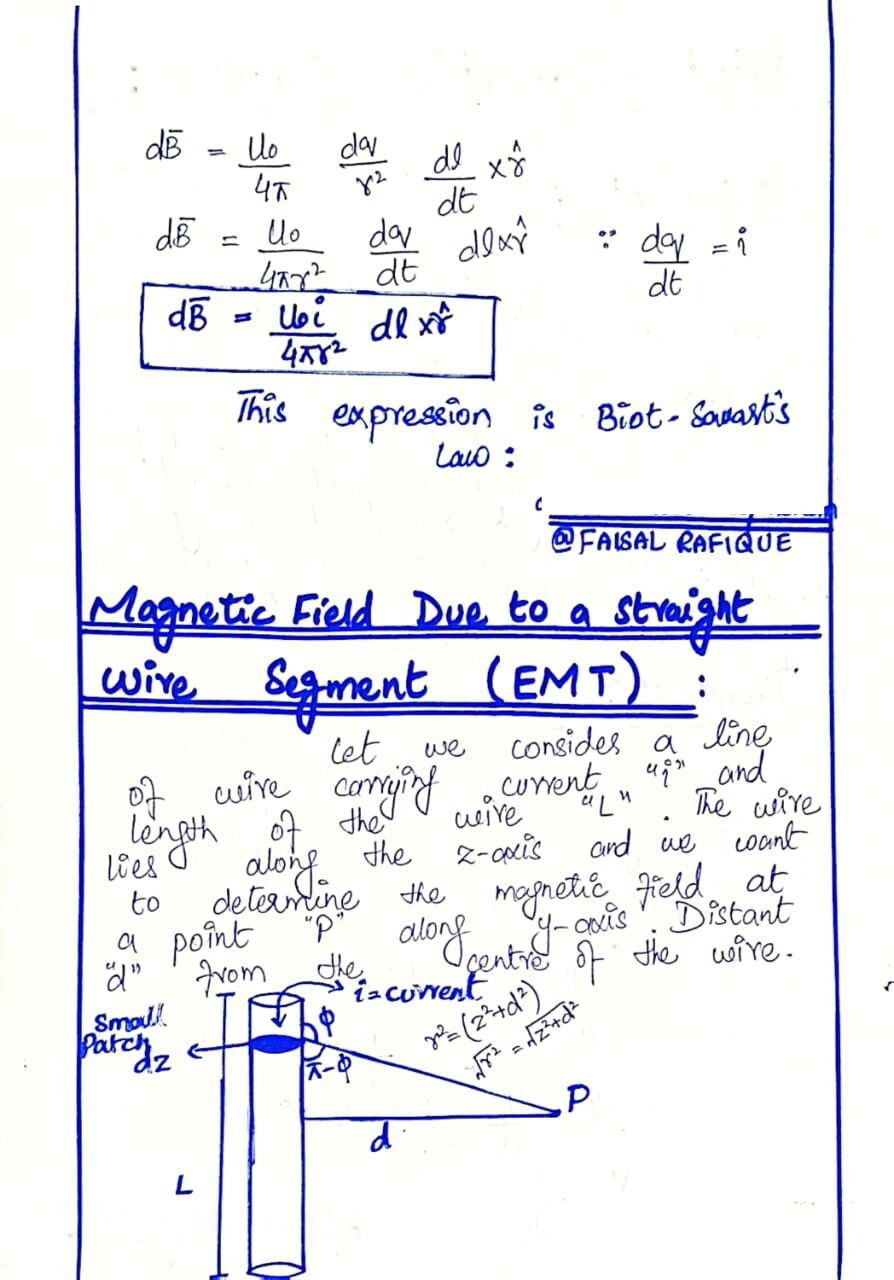
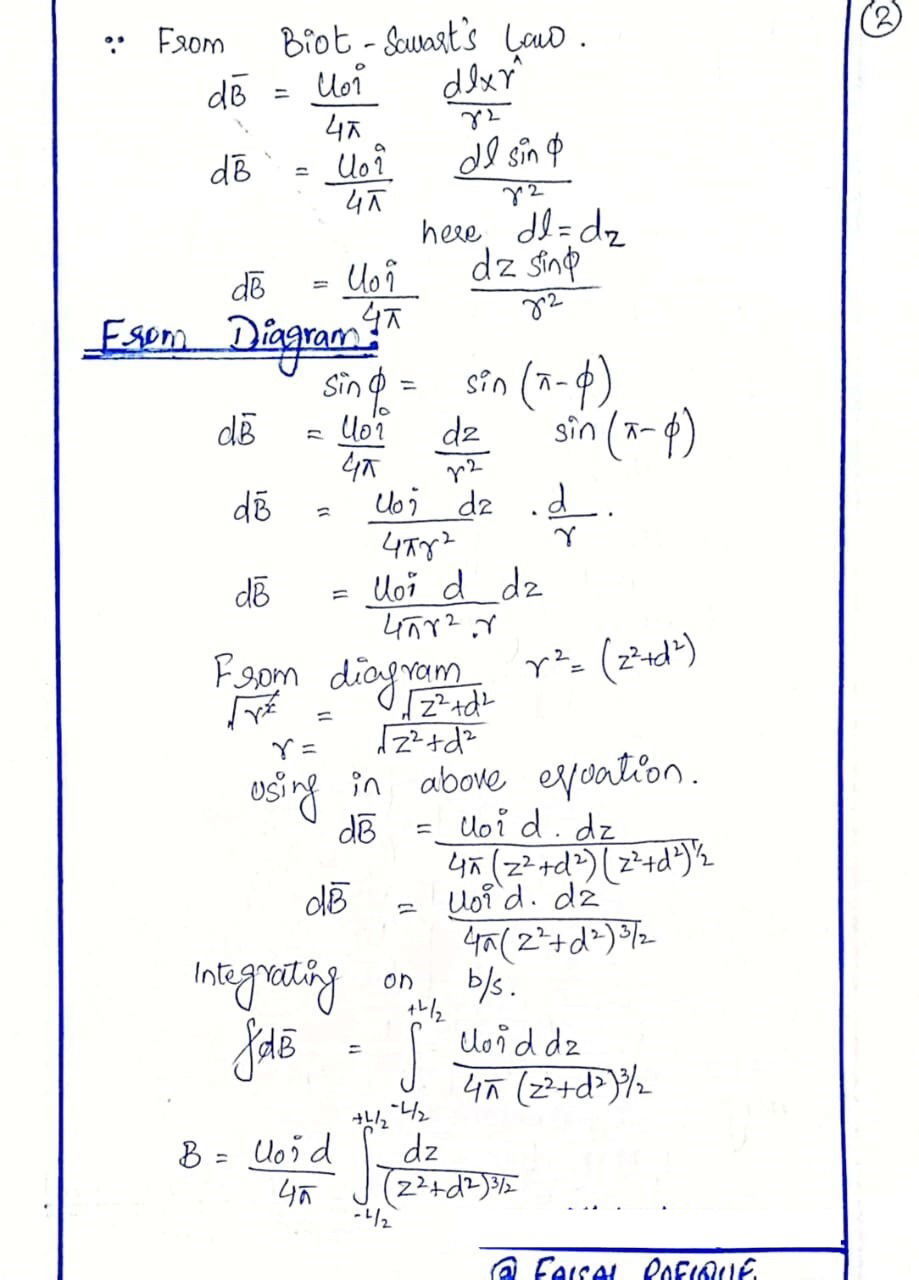
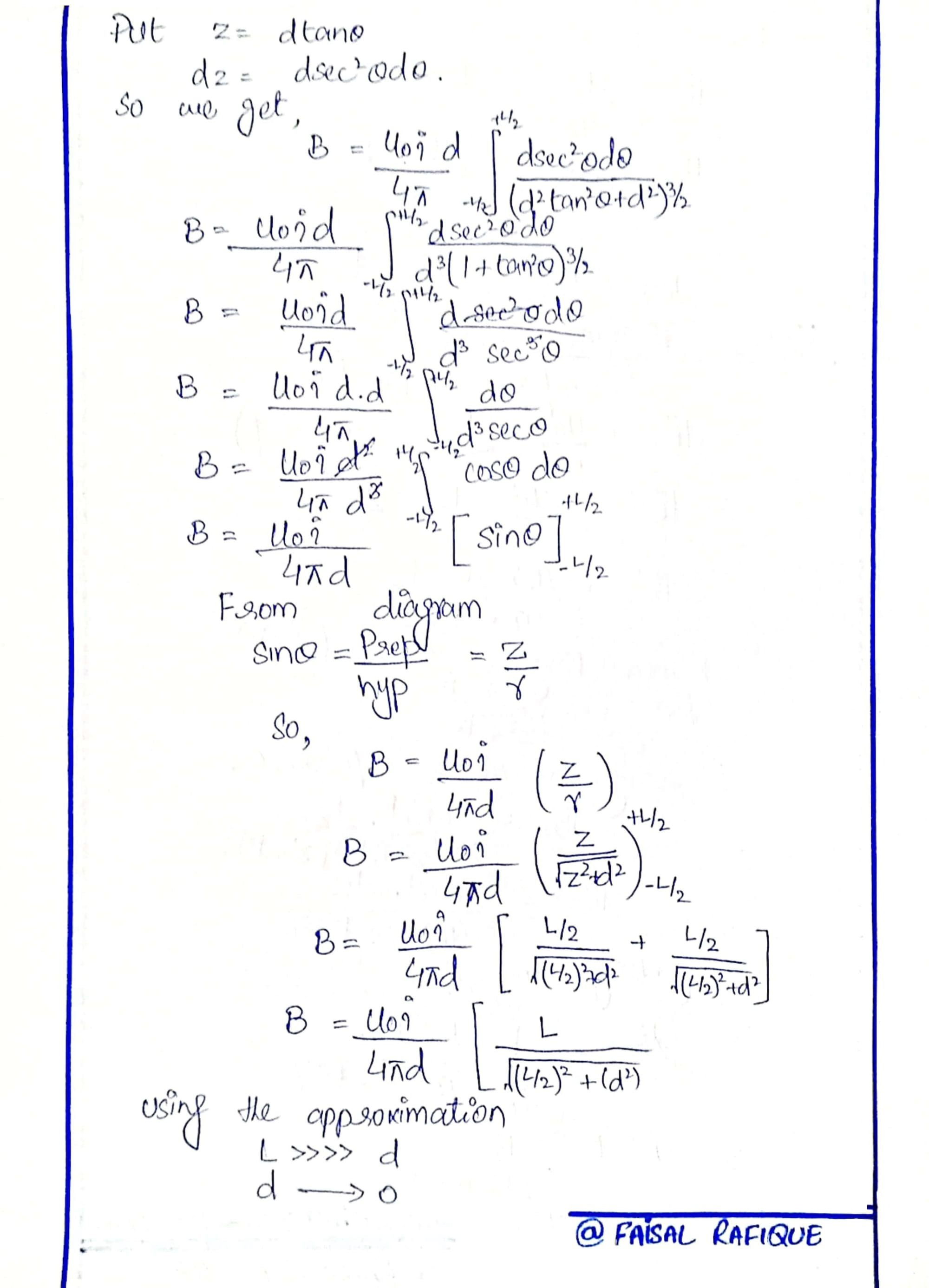
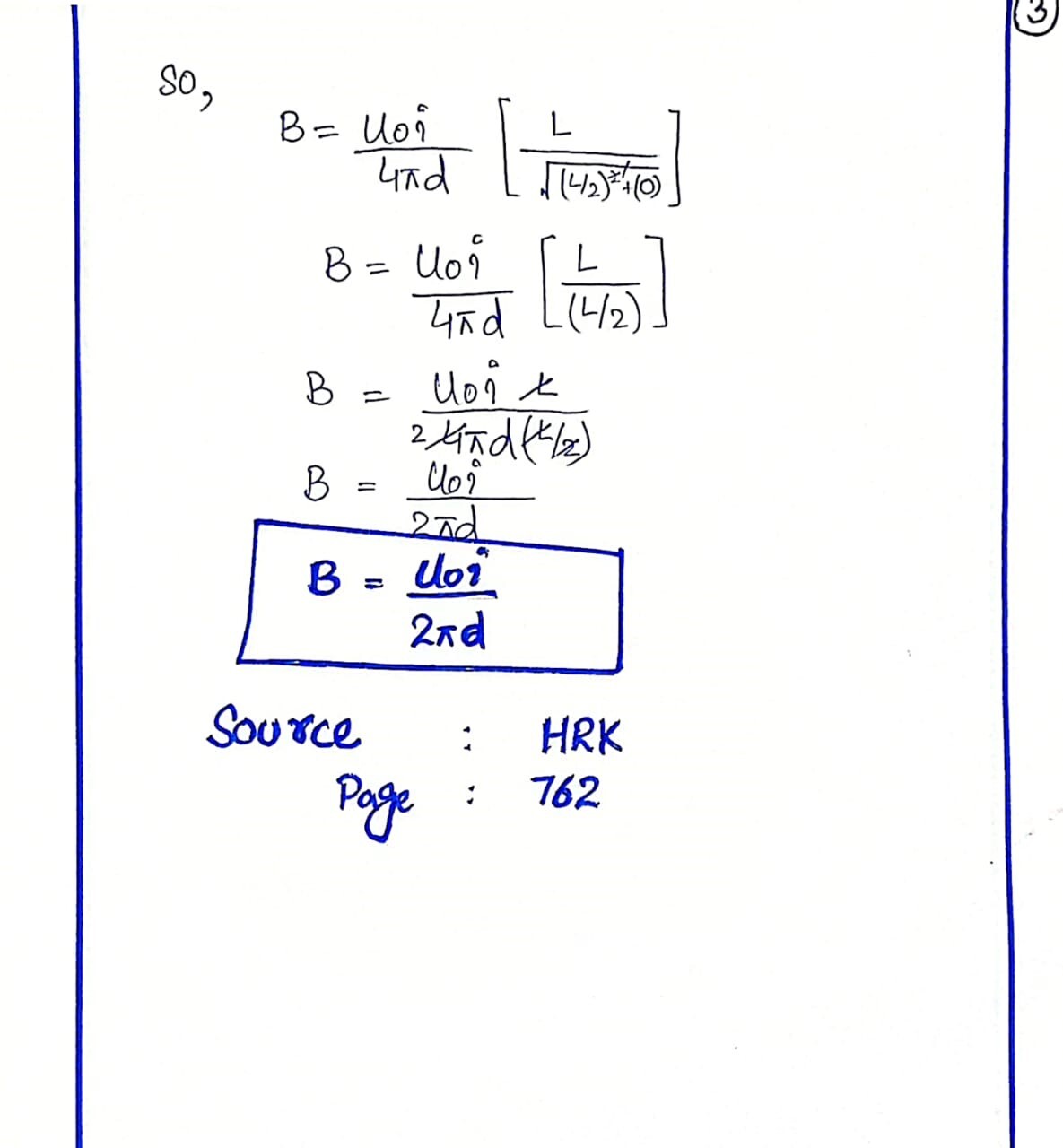
BIOT-SAVART LAW

Introduction :
The Biot-Savart Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the magnetic field generated by an electric current. Formulated by French physicists Jean-Baptiste Biot and Félix Savart in 1820, this law relates the magnetic field dB at a point in space to the current element Idl, the distance r between the current element and the point, and the angle θ between the current element and the vector connecting it to the point.
The Biot-Savart Law is a crucial concept in understanding electromagnetism, and it has numerous applications in fields such as engineering, materials science, and medical physics.

Comments