WHAT IS EARTH ?

INTRODUCTION :
- Earth is he third closest planet to The Sun.
- It is the only planet we have found that contains life.
- Earth is 4.543 billion years old.
- Earth's surface is mainly water.
- Earth rotates at around 1000 miles an hour.
- Earth's atmosphere is made of gases.
- Earth is not perfectly round.
- Distance from The Sun is 149.6 million km.
- Mass of The Earth is 5.972 *1024 kg
- Radius of The Earth is 6371 km
- Age of The Earth is 4.543 billion years.
- Gravity of The Earth is 9.8m/s2
- Surface Area of The Earth is 510.1 million km2
- Population of The Earth is 8 Billion as of 2024.
- Circumference of The Earth at Equator is 40,075 and at the poles 40,024 km.
- Equatorial radius of the Earth is 6,377 km.
- The total mass of the Earth is 5.98*1024kg.
- Approximate age of The Earth is 4500 million years.
- The mean velocity of the Earth in its orbit (around the Sun) is 107,218 km/h.
- The most abundant elements of The Earth are
- Iron (about 32.5%).
- Oxygen (29%).
- Silicon (15.6%).
- Magnesium (13.9%)
STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH :
The Earth is Structured in three layers namely
- Crust
- Mantle
- Core
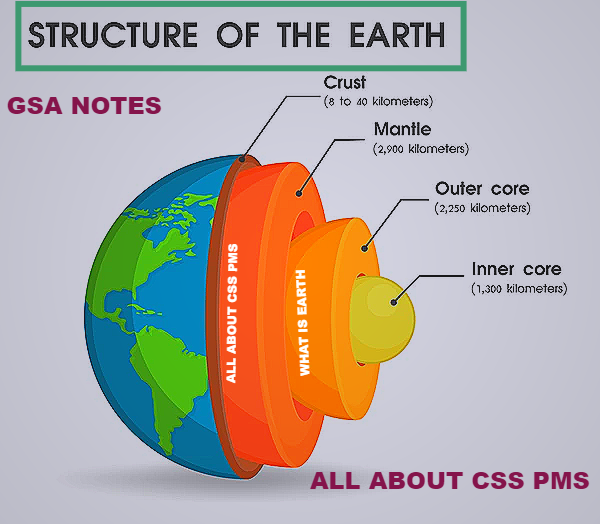
CRUST:
- The Crust is the uppermost layer of The Earth, largely composed of rocks. Its thickness ranges from 5km to 60km and density ranges from 2.7 to 3.
- The Crust shares about 1 percent of Earth's volume.
- The Crust is categorized as 'Continental Crust' and 'Oceanic Crust'.
- The thickness of Continental Crust ranges from 30 km to 50 km. It is largely composed by granites, which density (i.e 2.7) is lesser than the Oceanic Crust.
- The thickness of Oceanic Crust ranges from 5 km to 10 km and it is composed primarily of basalt, diabase, and gabbro.
- The most abundant element of Crust is Oxygen (46%) followed by Silicon (27.7%) and Aluminum (8.1%).
- The Crust is also known as 'Sial' ( i.e Silicon and Aluminum).
MANTLE :
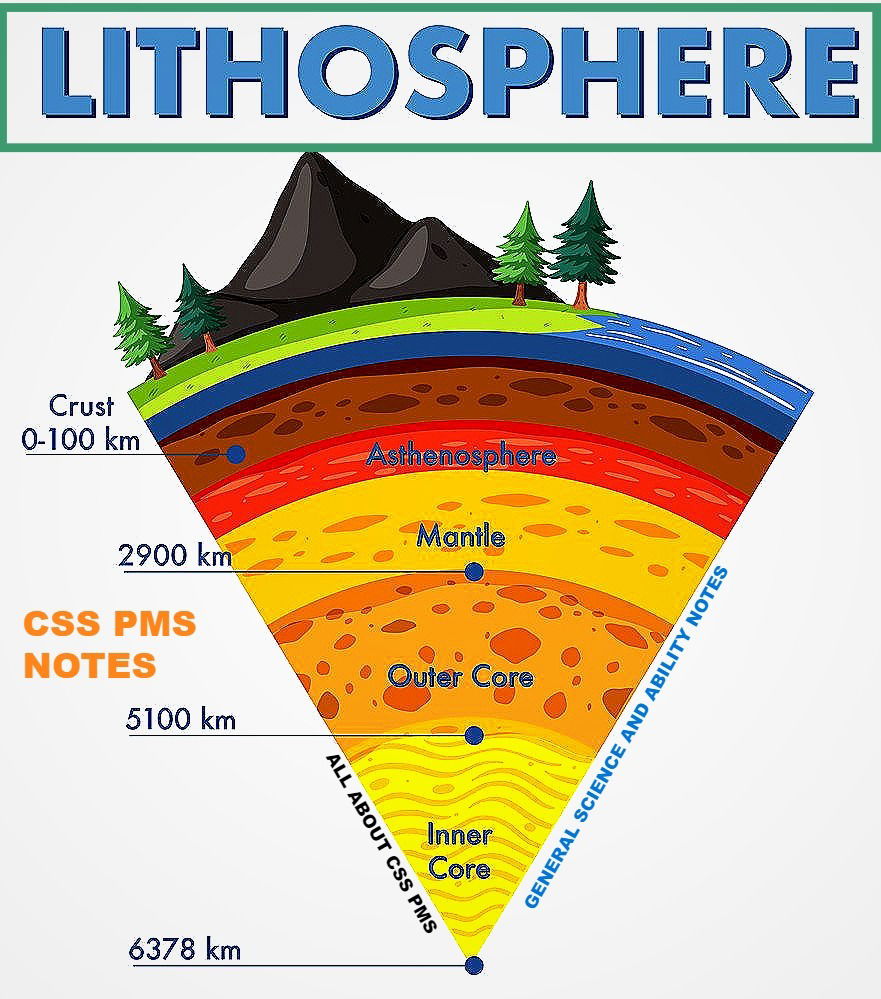
- The boundary between the Crust and the MAntle is known as the "Mohorovicic Discontinuity".
- The Mantle is located between the crust and the (outer) Core, which thickness is about 2885 km.
- the Mantle shares about 83% of The Earth's volume and about 65% of the mass.
- The density of Mantle is about 3.4g/cm3.
- The upper layer of Mantle is known as 'Asthenosphere'.
- The Crust and upper part of Mantle collectively known as 'Lithosphere'.
CORE :
- It is the central or inner most part of the Earth.
- The Core is mostly composed of iron and nickel; therefore, it is also known as 'Nife' (i.e Nickel and Ferrous).
- The Core shares about 16% of Earth's total volume and 30% of the mass.
- The thickness of the Core is about 3400 km from the Mantle (likewise, the total depth from the Surface of the Earth is 6300 km).
- Core is categorized as outer core (which is in molten state) and inner core (which is in solid state).
- Density of the inner core is about 13g/cm3.
How Old is Earth?
The Earth is estimated to be around 4.54 billion years old, based on radiometric dating of ancient rocks and meteorites. Scientists have analyzed isotopes of elements like uranium and lead in Earth’s oldest minerals, some of which date back 4.4 billion years. Meteorites, which formed around the same time as the solar system, also provide crucial evidence supporting this age. The oldest known rocks on Earth, found in regions like Greenland, Canada, and Australia, further confirm this timeline.
Earth formed from a swirling cloud of gas and dust surrounding the young Sun. Over millions of years, gravity pulled particles together, creating a molten, rocky mass. Intense volcanic activity, asteroid impacts, and a harsh atmosphere dominated its early years. Eventually, Earth cooled, forming a solid crust, oceans, and an atmosphere that could support life. Over billions of years, processes like plate tectonics, climate change, and evolution have continuously shaped the planet, making it the diverse and habitable world we know today.

Distance between Earth and Moon :
The Moon is, on average, 384,400 kilometers (238,855 miles) away from Earth. However, its distance is not constant because the Moon follows an elliptical orbit. At its closest point (perigee), the Moon is about 363,300 km (225,623 miles) away, while at its farthest point (apogee), it is around 405,500 km (251,966 miles) away.
This distance plays a crucial role in Earth's tides, climate, and even the stability of our planet's axial tilt. Interestingly, the Moon is slowly drifting away from Earth at a rate of about 3.8 cm (1.5 inches) per year due to gravitational interactions. Scientists have precisely measured the Moon's distance using laser reflectors left by Apollo missions, providing highly accurate data on its movement.
Distance between Earth and Sun :
The Sun is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles) away from Earth. This distance is known as one astronomical unit (AU) and serves as a standard measurement for distances within our solar system.
Since Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, the distance varies throughout the year. At its closest point (perihelion, in early January), the Sun is about 147.1 million km (91.4 million miles) away, while at its farthest point (aphelion, in early July), it reaches around 152.1 million km (94.5 million miles). Despite this variation, the difference in distance does not significantly affect Earth's seasons, which are primarily caused by the planet’s axial tilt.
How fast the Earth Spin :
The Earth spins on its axis at an incredible speed of approximately 1,670 kilometers per hour (1,037 miles per hour) at the equator. This rotational speed gradually decreases as you move toward the poles, where it becomes nearly zero. Despite this rapid motion, we don’t feel the Earth spinning because the atmosphere moves with it at the same speed, creating a stable environment for us.
Earth's rotation is responsible for the cycle of day and night, as different parts of the planet receive sunlight at different times. This rotation also plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns and ocean currents due to the Coriolis effect, which causes moving air and water to curve instead of traveling in a straight line. Interestingly, Earth's rotation is gradually slowing down due to the gravitational pull of the Moon, adding about 1.7 milliseconds to a day every century.

How long have humans been on Earth ?
Humans, specifically Homo sapiens, have been on Earth for about 300,000 years. Fossil evidence from Africa suggests that modern humans evolved around this time, gradually developing advanced tools, language, and social structures. These early humans spread across the globe, adapting to different environments and forming diverse cultures.
However, if we consider human-like ancestors, such as Homo habilis and Homo erectus, the timeline extends much further—millions of years. Homo habilis, one of the earliest members of the human genus, lived around 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago, while Homo erectus, who was more similar to modern humans, existed for nearly 1.9 million years before going extinct. Despite this long history, civilization as we know it—cities, agriculture, and written language—only began about 10,000 years ago with the advent of farming.