What is Eutrophication: Causes & Effects Explained
Introduction to Eutrophication
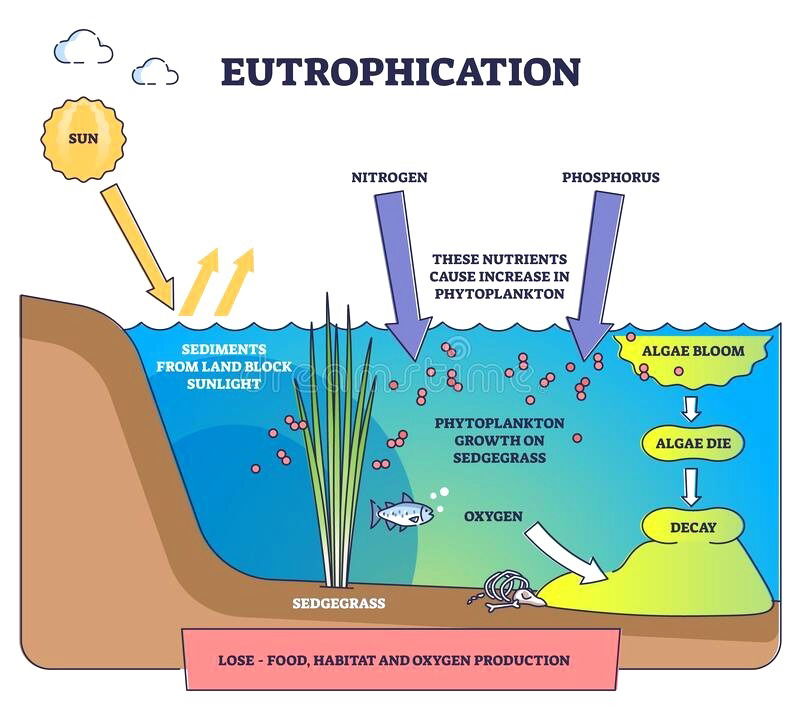
Eutrophication is a serious environmental issue impacting water bodies around the globe. It describes the rapid growth of plants and algae triggered by an overload of nutrients—especially nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus—in aquatic systems. This phenomenon is more common in lakes, canals, and shallow rivers than in deeper waters.
What is Eutrophication?
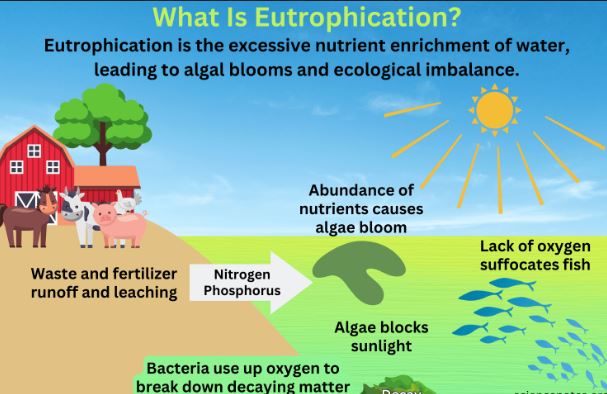
It is the process of excessive plant and algal growth in water bodies due to an influx of nutrients. This process leads to several environmental and ecological problems, including oxygen depletion and the degradation of water quality.
Key Nutrients Responsible for Eutrophication:
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
- Phosphorus
Types of Eutrophication
It can be classified into two main types:
1. Natural Eutrophication
A slow, natural process occurring over many years.
- Not influenced by human activities.
- Gradual accumulation of nutrients over time leads to ecosystem changes.
2. Cultural Eutrophication
A rapid process caused by human activities.
- Occurs within weeks or months.
- Accelerates natural eutrophication due to external nutrient sources.

Causes of Eutrophication
Many human activities are responsible for this problem. The main causes include:
- Excessive use of agro-chemicals (agricultural runoff containing fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides).
- Industrial waste disposal (discharge from fertilizer plants, food industries, and chemical production).
- Organic waste accumulation (livestock waste, sewage discharge, and decaying matter in water bodies).
- Deforestation and soil erosion (increases nutrient runoff into water bodies).
- Climate change and urbanization (alters natural water flow and increases pollution).

Process of Eutrophication
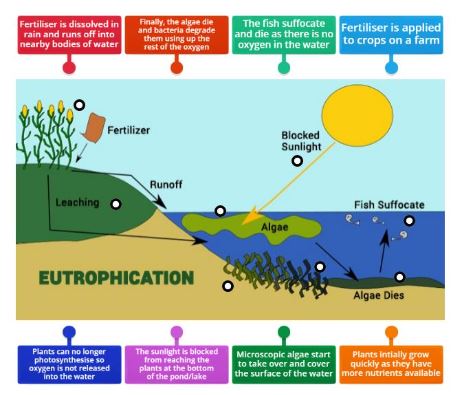
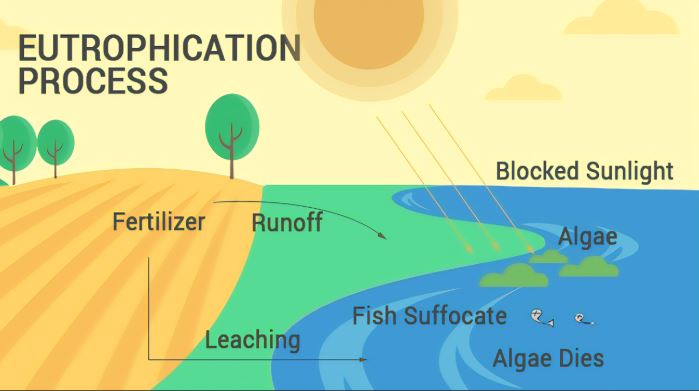
When fertilizers rich in nitrogen flow into water bodies, they trigger rapid growth of algae and aquatic plants. This thick plant layer blocks sunlight from reaching the bottom, killing smaller aquatic plants. As these plants die and decompose, they consume oxygen from the water leading to suffocation and death of fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Nutrient Enrichment: Fertilizers and waste introduce high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus into water bodies.
- Excessive Algal Growth: Algae multiply rapidly, forming dense algal blooms.
- Blocking Sunlight: Thick algal layers prevent sunlight from reaching underwater plants.
- Plant Death and Decay: Lack of sunlight kills smaller green plants, which begin to decompose.
- Oxygen Depletion: Decomposing organic matter consumes oxygen, leading to hypoxic (low oxygen) conditions.
- Aquatic Life Suffocation: Fish and other aquatic organisms suffocate due to low oxygen levels, causing massive die-offs.
Effects of Eutrophication
This issue causes many problems for lakes, rivers, the environment, and even human health. Some of the main effects include:
1. Environmental Effects
- Degradation of water quality (changes in physical properties, taste, and increased toxin levels).
- Disruption of aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity loss.
- Increase in harmful algal blooms (HABs), some of which produce toxins harmful to humans and animals.
2. Economic Effects
- Loss of fisheries and aquaculture due to fish kills.
- Increased water treatment costs.
- Decrease in tourism and recreational activities (due to bad odor, dead fish, and water pollution).
3. Public Health Risks
- Consumption of contaminated water may cause gastrointestinal diseases and other health disorders.
- Harmful algal toxins can lead to neurological and respiratory issues.
- Animals drinking contaminated water may suffer from poisoning or infections.

Real-World Examples by Country
1. Eutrophication in the USA - Lake Erie
One of the worst cases of eutrophication occurred in Lake Erie, where excessive fertilizer runoff led to massive algal blooms, affecting drinking water for millions.
2. Eutrophication in the UK - River Thames
Pollution and agricultural runoff have caused algal blooms in the River Thames, leading to oxygen depletion and fish deaths.
3. Eutrophication in Canada - Lake Winnipeg
Eutrophication in Lake Winnipeg has been a major environmental challenge due to increased phosphorus levels from urban and agricultural sources.
4. Eutrophication in Australia - Murray-Darling Basin
Eutrophication events have led to toxic blue-green algae outbreaks, harming aquatic ecosystems and water quality.
5. Eutrophication in India - Vembanad Lake
Agricultural and industrial waste discharge has caused severe eutrophication in Vembanad Lake, impacting local biodiversity and fisheries.
Solutions to Prevent Eutrophication
Solving this problem needs strong laws, eco-friendly habits, and public support. Some of the best ways to fix it include:
- Reducing Agro-Chemical Usage: Implementing controlled fertilizer applications and alternative organic farming techniques.
- Proper Waste Management: Developing separate mitigation systems for agricultural runoff and sewage treatment.
- Physical Algae Removal: Harvesting algae manually for potential uses like biodiesel production.
- Strengthening Environmental Institutions: Implementing strict regulations on industrial discharge and wastewater treatment.
- Public Awareness and Education: Promoting sustainable water management and conservation practices.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Aligning with global sustainability targets to ensure long-term water resource management.
- Restoring Natural Vegetation: Planting buffer zones and wetland restoration to absorb excess nutrients before they enter water bodies.
Conclusion: Why Tackling This Water Crisis Matters
This isn’t just a science problem — it’s a hidden danger to clean water, wildlife, farming, and human health. Around the world, toxic algae are spreading and oxygen levels in lakes and rivers are dropping fast.
If left alone, this issue can turn clean, living water into dead zones. It can harm animals, hurt local communities, and make water unsafe to drink. But there’s hope — this damage can be stopped.
With better farming, strong waste control, clear laws, and public action, we can protect our lakes, rivers, and wetlands. This isn’t just about nature — it’s about our future. Solving this problem now means cleaner water, stronger ecosystems, and safer communities for generations to come.
Protecting our lakes, rivers, and wetlands is no longer optional—it’s essential for sustainable living and future generations. Tackling eutrophication today means securing clean water, healthy ecosystems, and resilient communities tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is eutrophication in simple words?
When a water body gets too many nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, causing plants and algae to grow too fast, which harms aquatic life.
2. What causes eutrophication?
Main causes include agricultural runoff (fertilizers), sewage discharge, industrial waste, and deforestation that lead to excess nutrients in water.
3. What are the effects of eutrophication?
It leads to algal blooms, oxygen depletion, fish kills, poor water quality, bad smell, and health risks for humans and animals.
4. Can eutrophication be stopped or reversed?
Yes. Through better farming practices, proper waste management, restoration of wetlands, and environmental regulations, It can be slowed down or even reversed.
5. What is cultural eutrophication?
It’s a fast, human-induced form of eutrophication caused by pollution and nutrient-rich waste entering water bodies.
6. Which countries are most affected by eutrophication?
The USA, UK, Canada, Australia, India, and China have faced serious eutrophication problems in lakes, rivers, and coastal areas.
👉 Want to explore more? Read our complete guide on Water Pollution here Click here